Anthem – AdvaNced Technology for Human centrEd Medicine is an initiative funded by the Ministry of University and Research as part of the National Complementary Plan (PNC) to the PNRR (https://fondazioneanthem.it/)
Anthem, selected together with three other Initiatives following the call for proposals referred to in Directorial Decree no. 931 of 06-06-2022, has a duration of 48 months, has received funding of € 123,477,500.47 (D.D. no. 1983 of 9-12-2022) and is structured as a Foundation that includes 23 National Entities. ANTHEM aims to fill, with the help of multidisciplinary and innovative technologies and pathways, the existing gap in the health care of frail and chronic patients within specific territories, affected by orphan diseases. It deals with the following areas of research and development:
Smart monitoring: Development of new sensors and technologies (or the improvement of existing ones) to monitor patients and fragile subjects, ensuring the continuous and real-time collection of data and their integration with environmental monitoring systems, to reduce the pressure on hospital centers and reduce the geographical gap.
Prevention and diagnosis: Development of new Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies and methodologies capable of improving diagnostics, making innovations scalable downwards and therefore exportable to every area of the country, to increase the ability to prevent a whole range of diseases, identifying early signs of worsening health conditions.
Personalized treatments: Improvement and increase of personalized medicine pathways, providing for the development of advanced treatments for orphan diseases, such as some cancers with a short life expectancy, or chronic pathological conditions. These new treatments are calibrated to the characteristics of the patient (socio-economic status, autonomy, family support) and the territory of residence.
Technological improvement and transferability: Transferability of technological improvements achieved, for example, by ensuring data protection and interoperability with new or existing technological platforms.
These topics are addressed within 4 project Spokes, headed by the University of Milan Bicocca, which represents the Hub for the management and coordination of the initiative. Each Spoke organizes its activity in Pilots with different objectives.
The Italian National Institute of Nuclear Physics (INFN) participates in Spoke 4 and Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) is the topic of Pilot number 9. The goal is the construction of a research and clinical facility for the application of BNCT at the University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli”. The National Laboratories of Legnaro, the Southern National Laboratories, and the Units of Pavia, Naples and Turin are participating in this project. The construction of the centre is not only funded by the PNC-PNRR but also by the Government of the Campania Region through the University “L. Vanvitelli”.
The new BNCT infrastructure is based on technology developed by INFN to produce an intense neutron beam from an accelerator (RFQ, see Fig.1) capable of generating a 5 MeV, 30 mA proton beam, coupled to a beryllium target and a neutron moderation and collimation system (BSA). This technology, entirely designed and built by INFN, will be the heart of a center that will serve as a hub for BNCT research and for the treatment of tumors that have a poor response to other therapies such as, for example, Glioblastoma Multiforme.
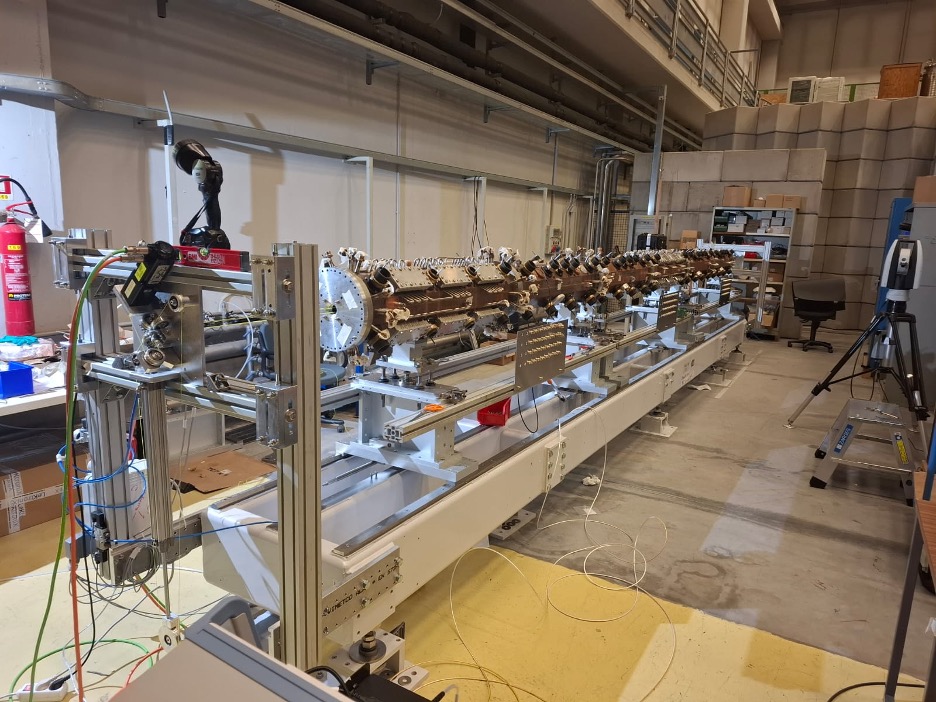

Figure 1: the RFQ accelerator mounted on the support at the Legnaro National Laboratories
University of Campania “L. Vanvitelli” oversees the design of the building that will contain the accelerator and the research and treatment rooms, as well as the laboratories and rooms for patient preparation. The design of the building has been realized by the Company Alcotec (https://alcotec.it/).
Figure 2 shows the rendering of the centre, located in an area where other installations will be constructed.
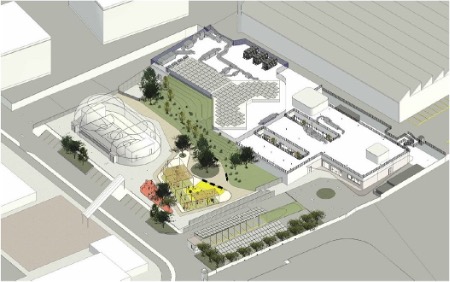
Figure 2: rendering of the BNCT installation with other facilities in the area.
Figure 3 shows the layout of the centre, comprising the technical areas (for the accelerator and its ancillaries), the irradiation room for patients, the room for research experiments, the areas for patients preparation, the laboratories and the room for post-irradiation.
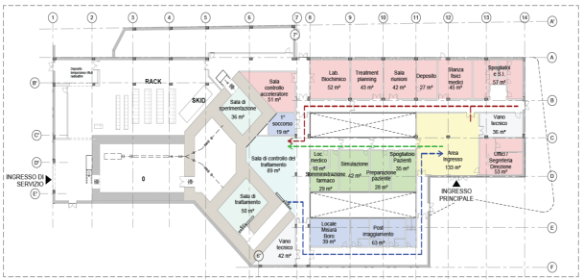
Figure 3: Layout of the facility.
Figure 4 shows the 3D rendering of the building with the accelerator and its ancillaries.
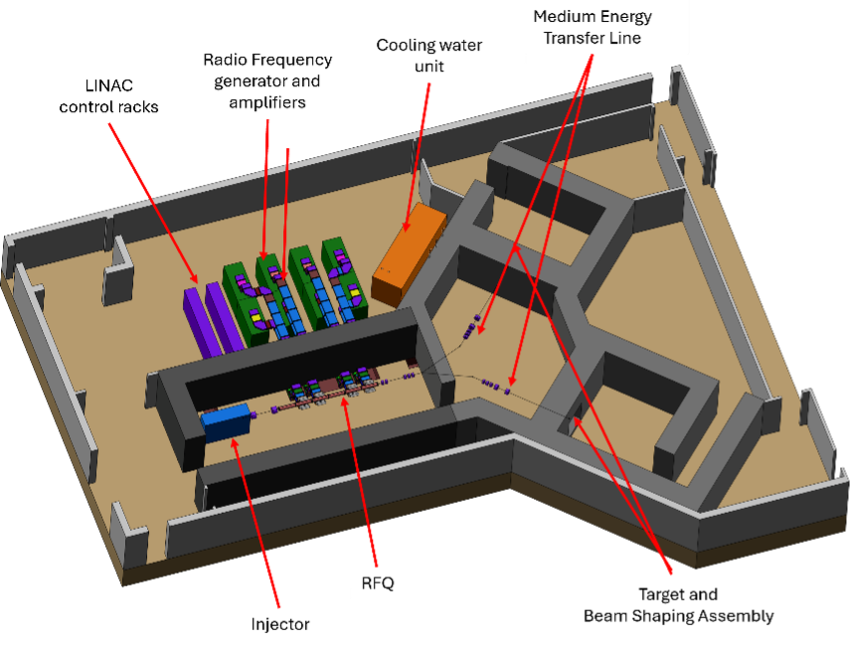
Figure 4: 3D structure of the BNCT installation with the technology installed
Thanks to the long research experience in BNCT carried out in Italy, and with several international collaborations, the goal is to promote global innovation in BNCT, integrating different aspects that are normally addressed separately. The vision is to exploit the knowledge generated in basic research and technological development in a more structured way. BNCT is a complex field, where treatment efficacy depends on the interaction between various factors, including the physical quality of the beam, the radiobiological response of the irradiated tissue, and the specifics of the treatment plan.
Particular attention will be given to the implementation of more refined dosimetry and microdosimetry methods, able to interpret and predict the clinical results obtained in previous studies, and to the production of new radiobiological data useful to better understand the dose-effect relationship in BNCT. Models and data will be integrated into the treatment planning software, which will allow for more personalized and precise dosimetry.
A real innovation in BNCT can only derive from the knowledge produced through basic research and a significant improvement will be obtained by systematizing and coherently applying the important information acquired so far, representing a significant step towards a new clinical reality in Italy.