Authors:
Claudio Andenna(A),Barbara Caccia(B) with the support of Pablo Cirrone (LNS-INFN Catania, Italy).
A) ISPESL and INFN Roma, gruppo collegato Sanità, Italy
B) Istituto Superiore di Sanità and INFN Roma, gruppo collegato Sanità , Viale Regina Elena 299, 00161 Roma (Italy)
Introduction
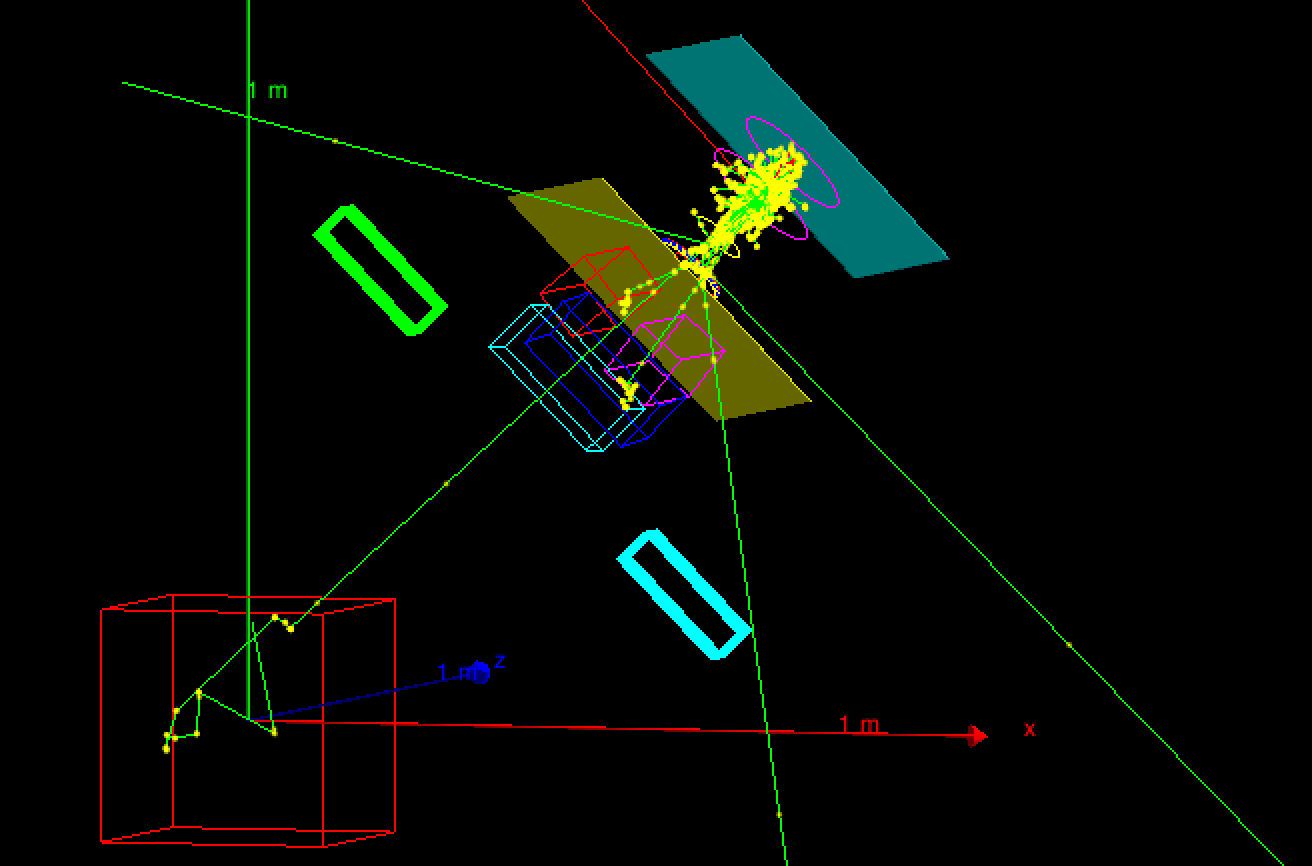
The example is based on a typical structure of a medical linear accelerator for Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT), such as Varian Clinac 2100 accelerator. The user may choice a cubic phantom filled with water or a phantom filled with an equivalent lung-tissue with a inhomogeneity (a 6 cm sided PMMA cube) located in the centre of the phantom. Two type of particle sources may be chosen, a random generator of electrons gun shooting the target or particles loaded from a phase space. The program allows the generation of a plane phase space. However since the mother volume of this plane phase space is the accelerator volume it can be positioned only inside the accelerator main volume.
Experimental set-up
The elements simulated are:
A source of electrons (the distribution of the electron energy and the electron radial intensity was assumed Gaussian in direction and energy). The beam direction is along the z axis.
A target
A primary collimator
A vacuum window
A flattening filter
A ion chamber
A mirror
A light field reticle
Secondary movable collimators (jaws)
A simple Multi Leaf Collimator
Phantom1 ("fullWater") filled with water (cube of 60 cm sided)
Phantom2 ("BoxInBox") filled with G4_ICRP lung tissue (cube of 30 cm sided) with a inhomogeneity (PMMA 6 cm sided cube) in the centre and a PLEXIGLASS slab 1 cm thick on the surface of the phantom.
The distance between the target and the surface of the phantom (SSD) is 100 cm.
Setting up the environment variables
The program uses two environmental variables called "ML2MYFILEIN" and "ML2MYFILEOUT" for the input and output files respectively.
If these environmental variables are not set the program works on the current directory
How to run the example.
The example runs with the ml2.mac macro file.
This file contains some setup information and in particular the name of other two macro files ("phan1.mac" and "acc1.mac") describing the chosen phantom and accelerator.
Inside the ml2.mac file there is a flag "/OnlyVisio" that has to be set "true" to switch on the visualization mode calling the "vis.mac" file ("false" for the modality without visualization).
Physics processes and physics model implementation
The ML2Physicslist class allows the activation of all the physic models either using the physics lists or the physics package lists. The standard electromagnetic option3 model is the default model.
Simulation output
The output of the ML2 example is:
A phase space file containing the data of the particles hitting the plane phase space. The file contains:
a progressive number, position, direction, kinetic energy, PDGE code of the particle, PDGE code of the primary particle, progressive number of the primary particle generating the event in the phase space
An output file written in matlab format generated from an experimental data file (if provided). The file contains:
position of the voxels and experimental dose values as given in the experimental data file, cumulative dose, cumulative square dose, number of events in the voxels, cumulative dose normalized to the experimental data (if provided), cumulative square dose normalized to the experimental data (if provided)
An output file containing the ROG results. The file contains:
name of the physical volume, position, indexes of the voxel according to the voxelization of the ROG, cumulative dose, cumulative square dose, number of events in the voxel