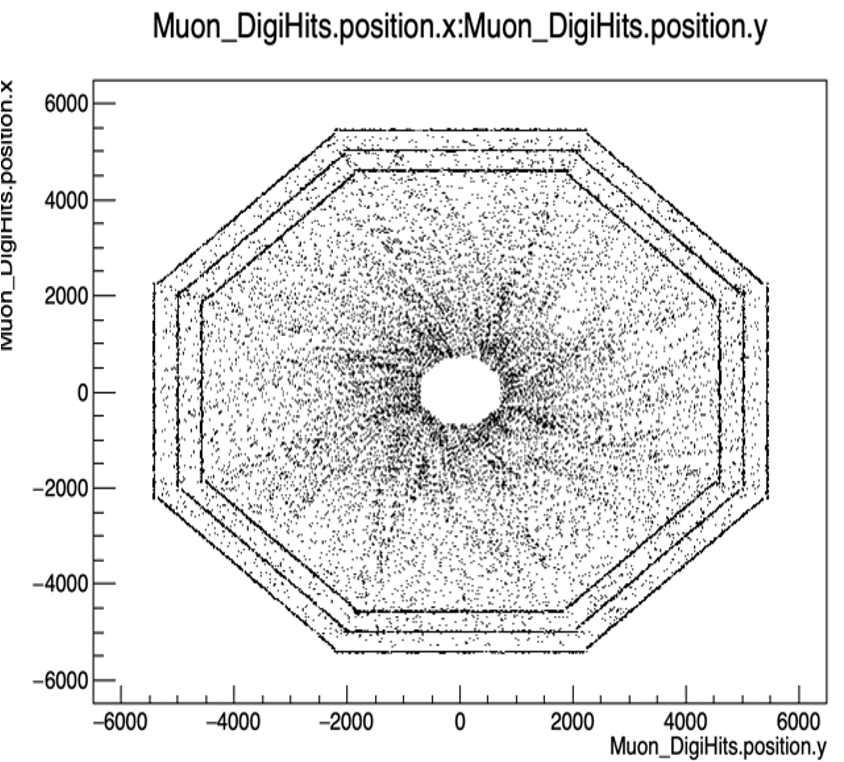
The Muon detection system will adopt the IDEA geometry, featuring a cylindrical barrel with endcaps to ensure hermeticity. It will include three or more detector layers within the iron yoke surrounding the solenoidal magnetic field.
Preliminary simulations show that muons from Z0 decays experience a positional accuracy loss of a few millimeters due to multiple scattering, while those from long-lived particle (LLP) decays in the calorimeter have a smaller loss, around hundreds of microns. In addition to these effects, a momentum measurement performance has also been considered. A spatial resolution of a hundred microns is required to achieve the precision necessary for an accurate momentum reconstruction of LLPs.
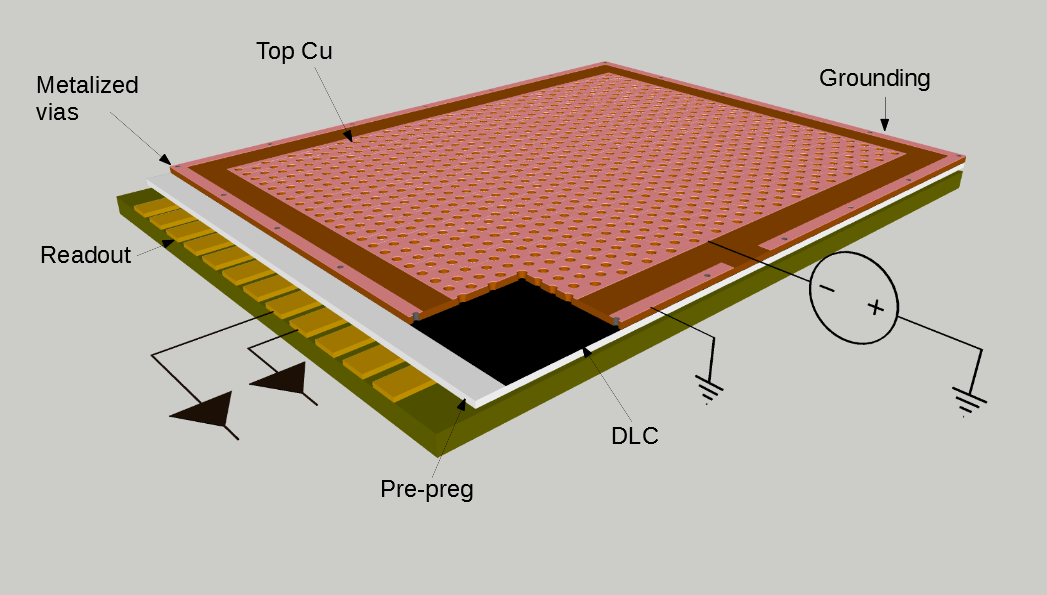
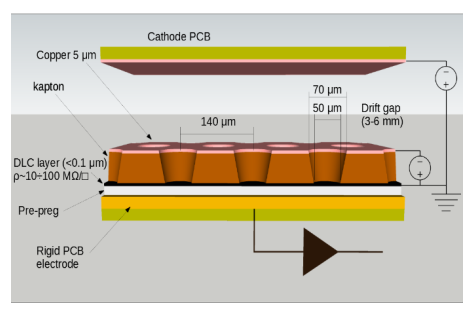
To fulfill the required space resolution, the muon system will utilize µ-RWELL detectors [1], an innovative, single-stage, and compact gaseous detector belonging to the Micro-Pattern Gaseous Detector (MPGD) family.
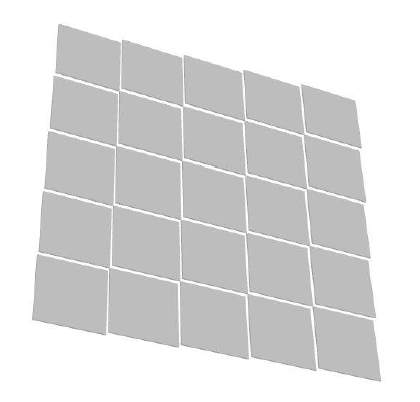
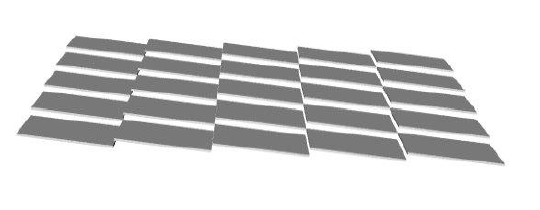
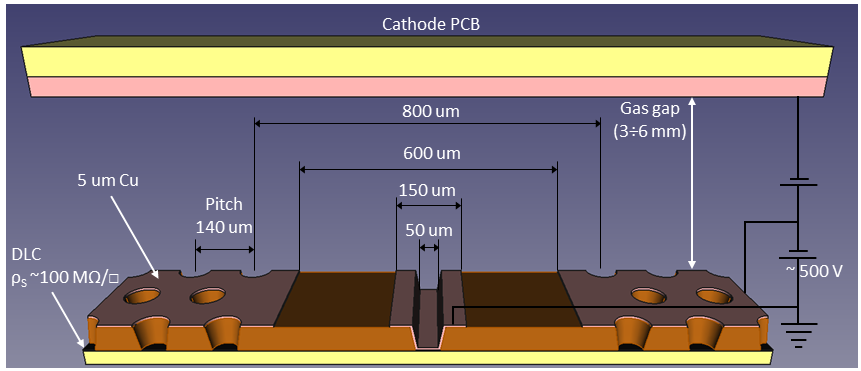
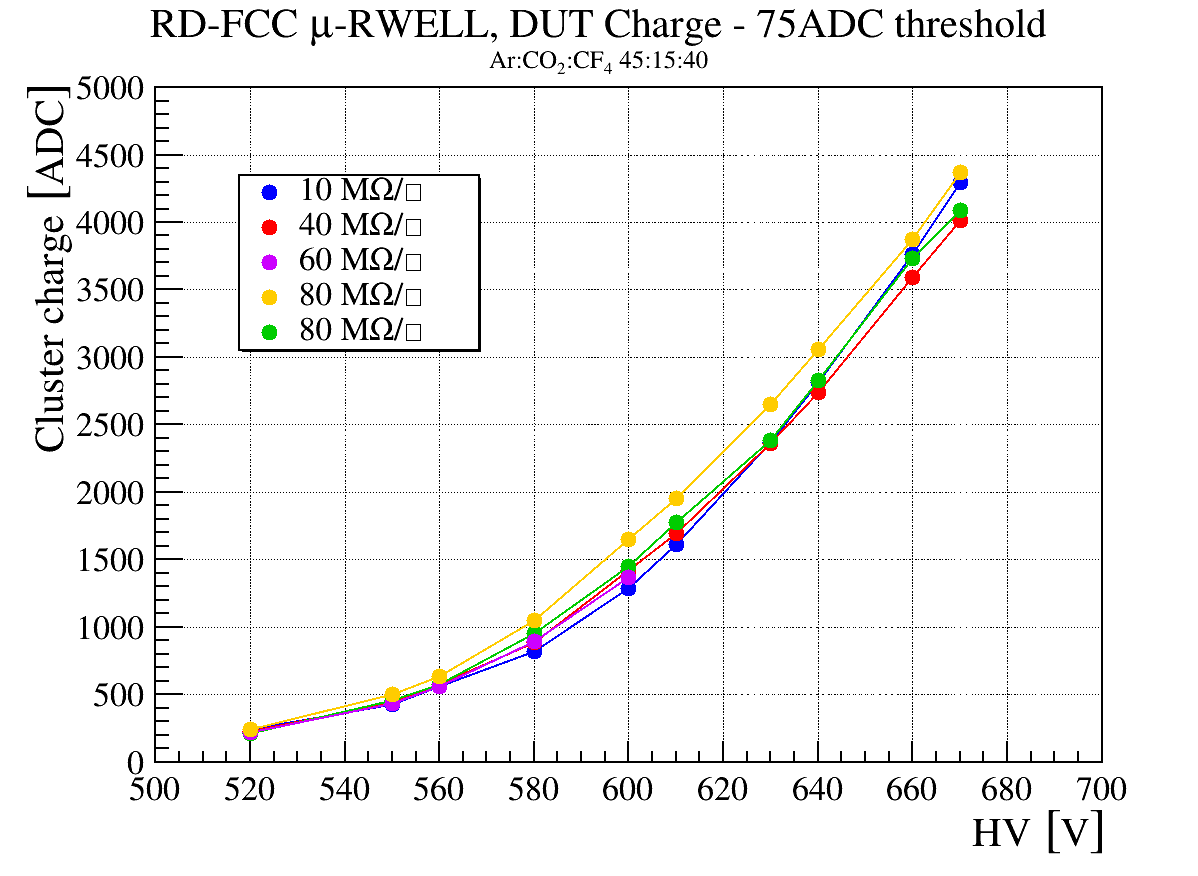
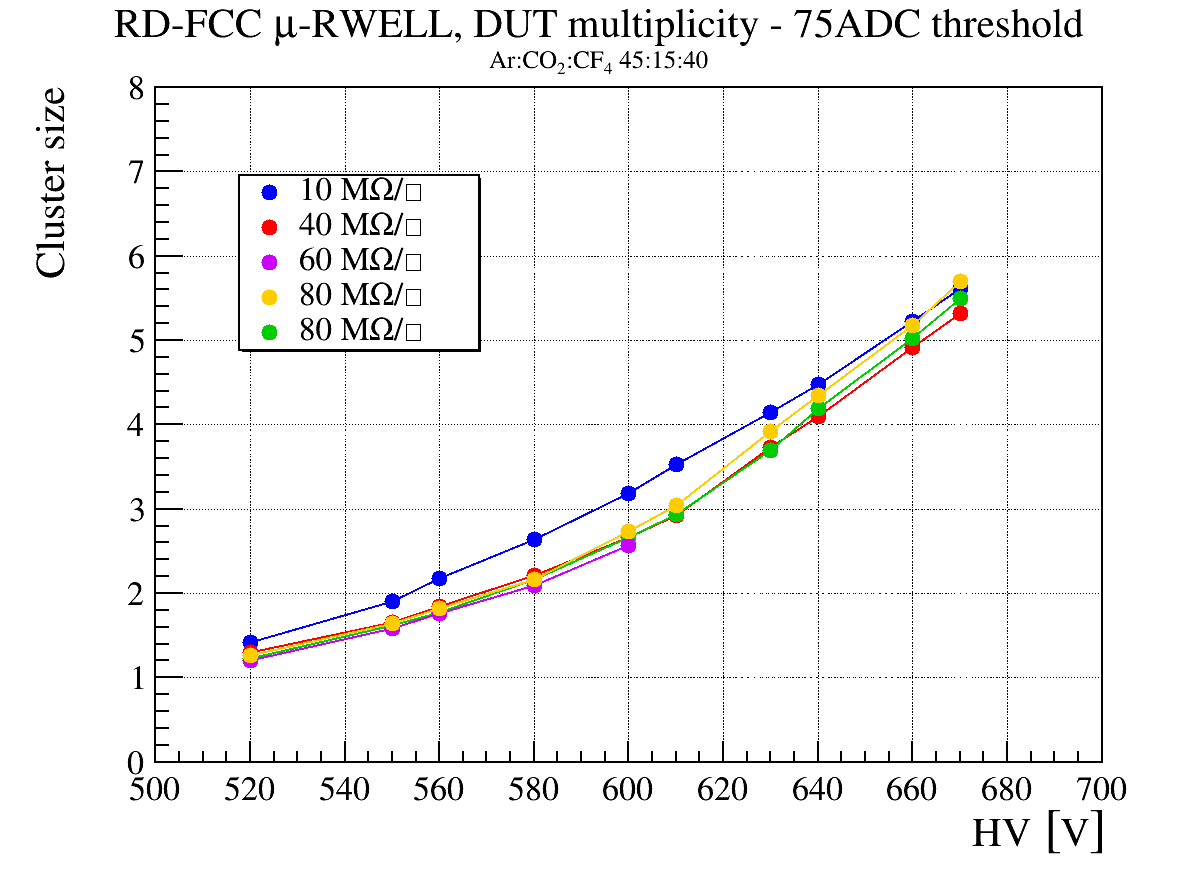
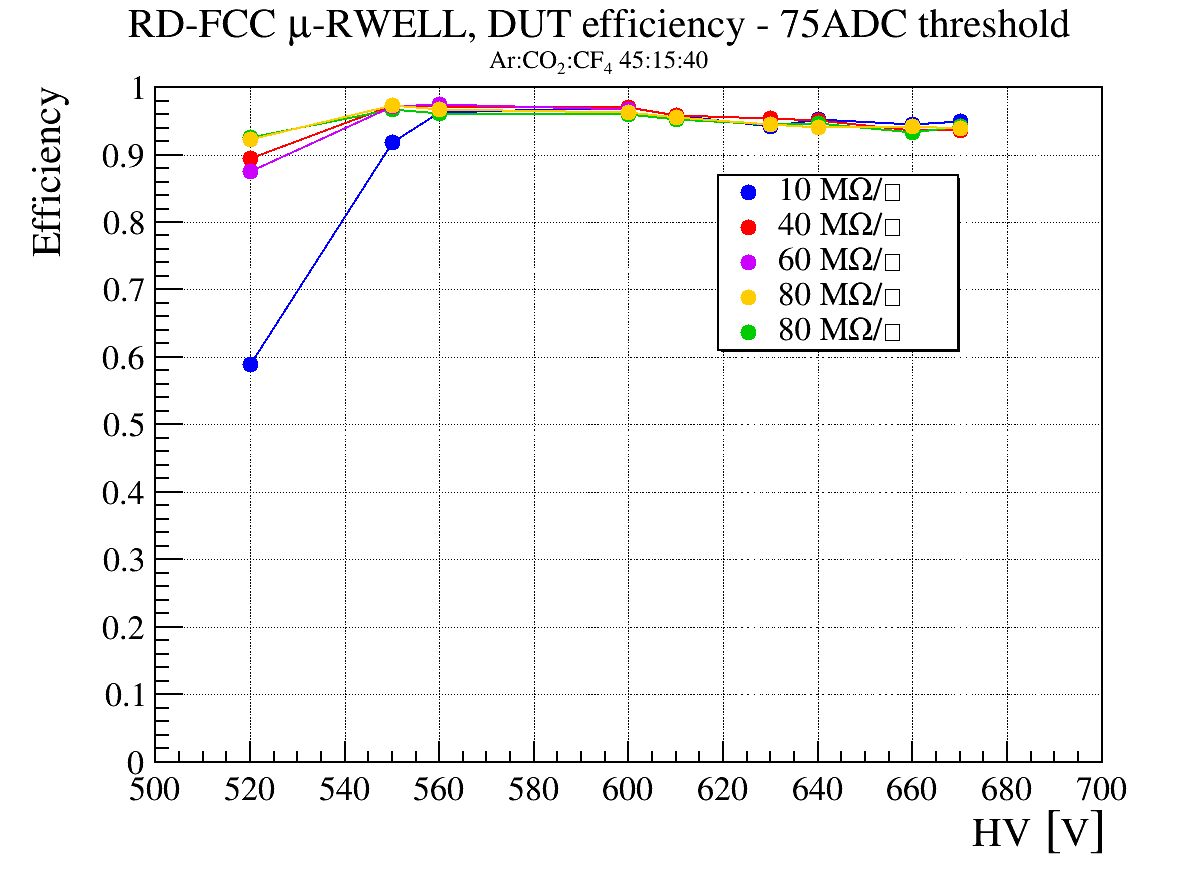
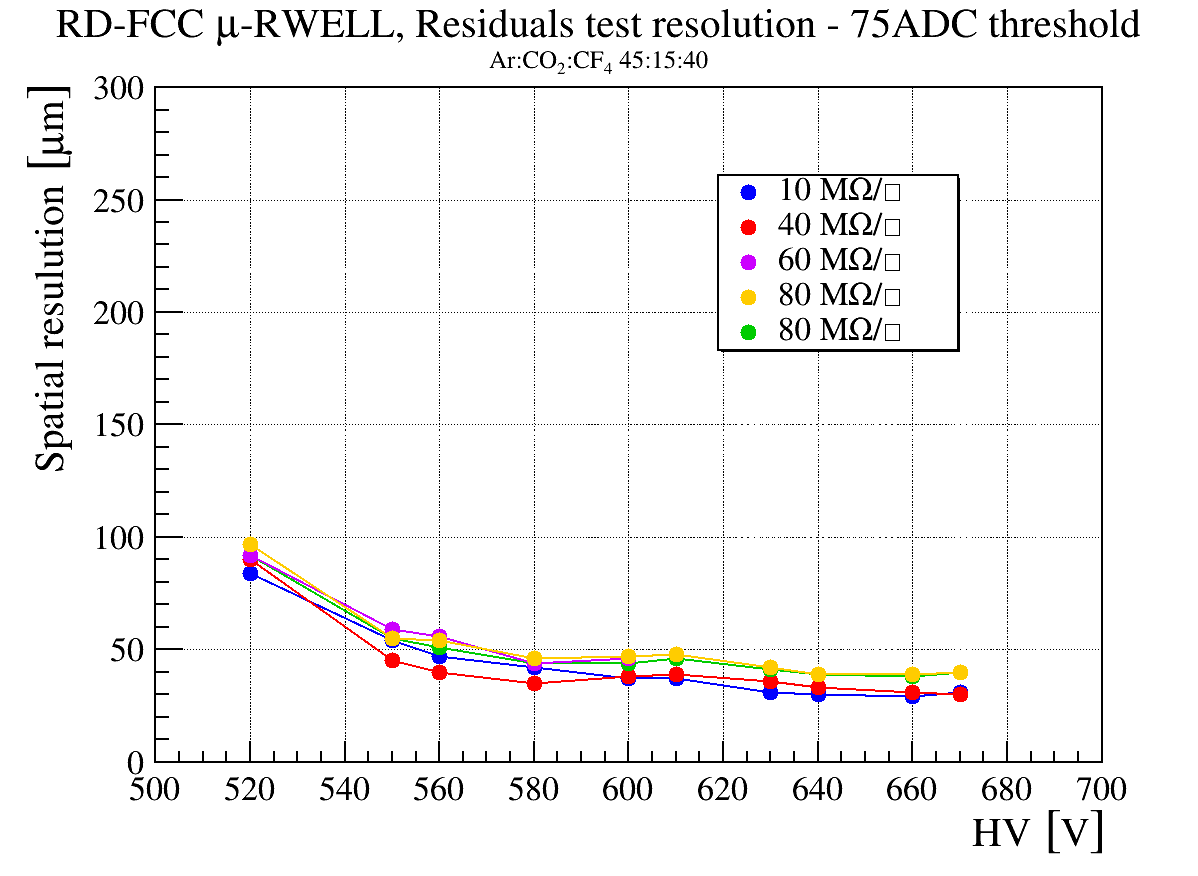
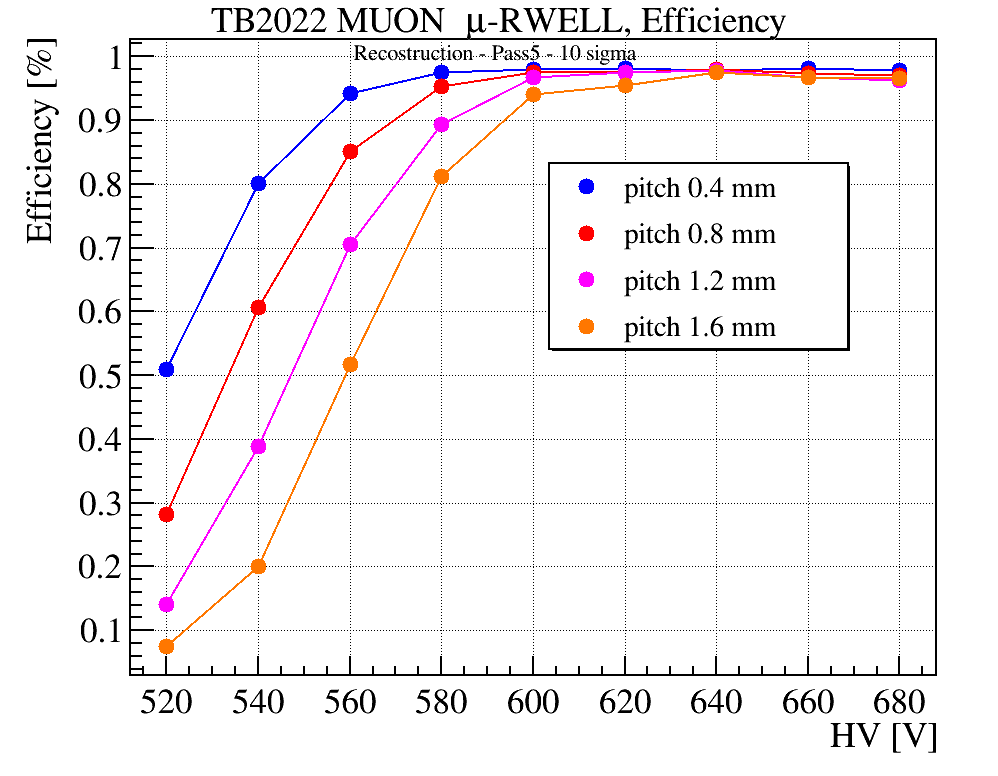
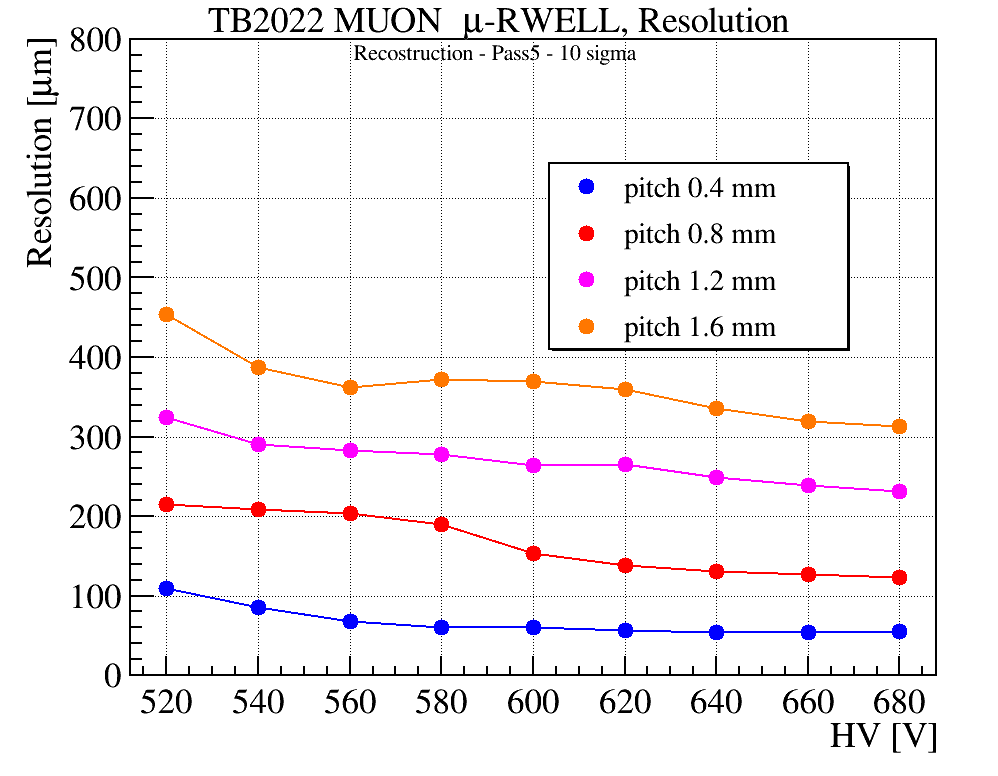
To take advantage of the industrial production capabilities of this technology, a modular design has been adopted. Each basic µ-RWELL tile features an active area of 50×50 cm2 with a two-dimensional strip readout. Strip pitches ranging from 0.4 to 1.5 mm provide spatial resolutions between 100 and 500 µm, corresponding to 640–2500 readout channels per tile. The choice of tile size, strip pitch, and strip width balances several factors: the largest µ-RWELL size feasible for mass production, the maximum input capacitance tolerable by the Front-End Electronics (FEE) to ensure an adequate signal-to-noise ratio, the spatial resolution required by the experiment, and the need to keep readout electronics costs within budget constraints.
[1] G. Bencivenni, R. De Oliveira, G. Morello, and M. Poli Lener, “The micro-resistive WELL detector: a compact spark-protected single amplification-stage MPGD”, JINST 10 (2015) 02, P02008
INFN Activities
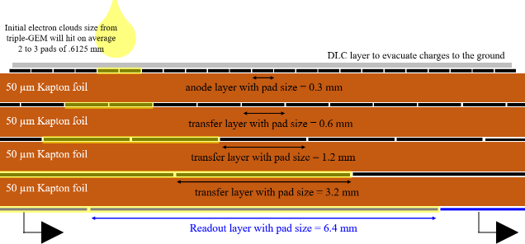
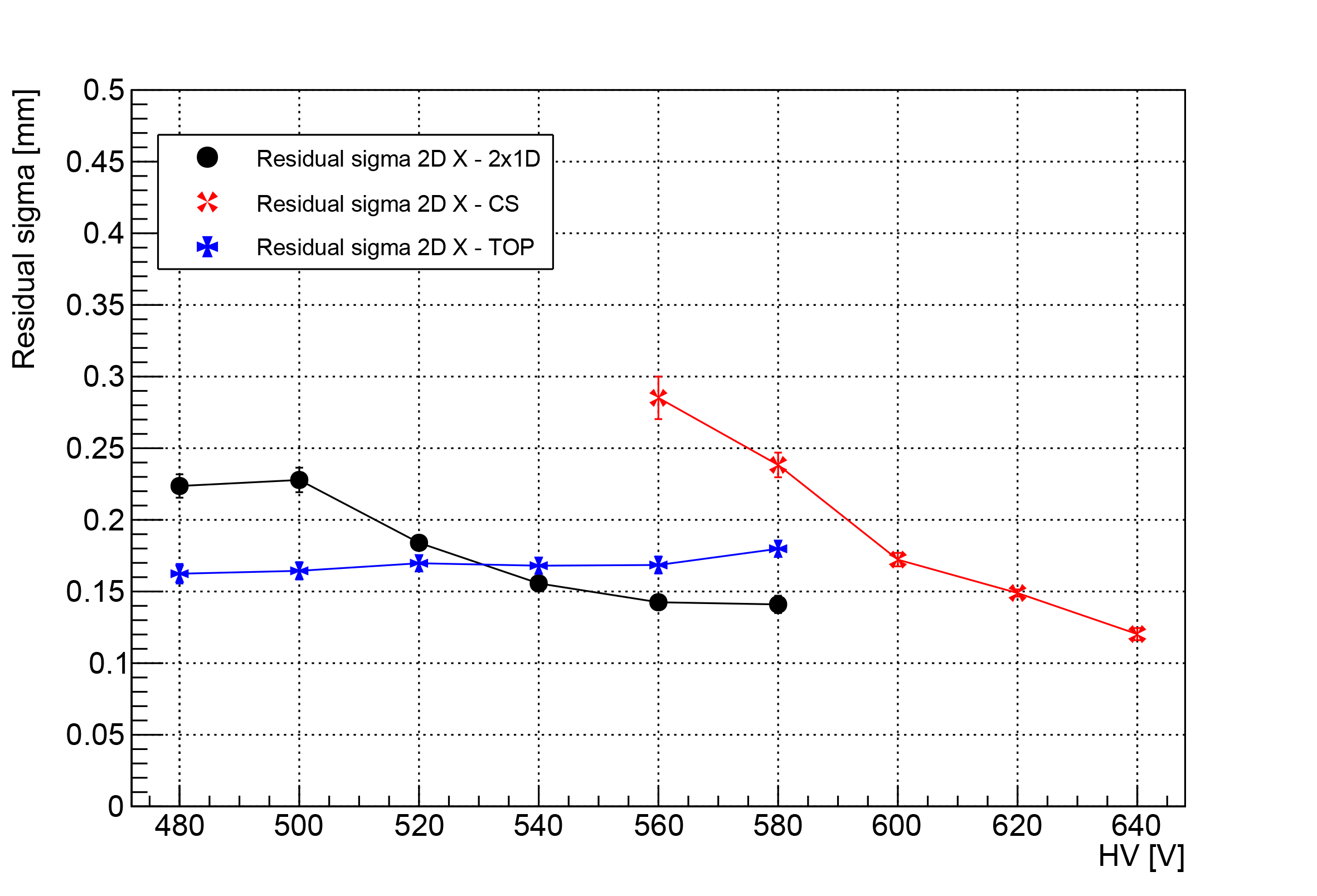
In recent years, the R&D program has focused on developing a two-dimensional µ-RWELL layout with strip readout for the Muon system.
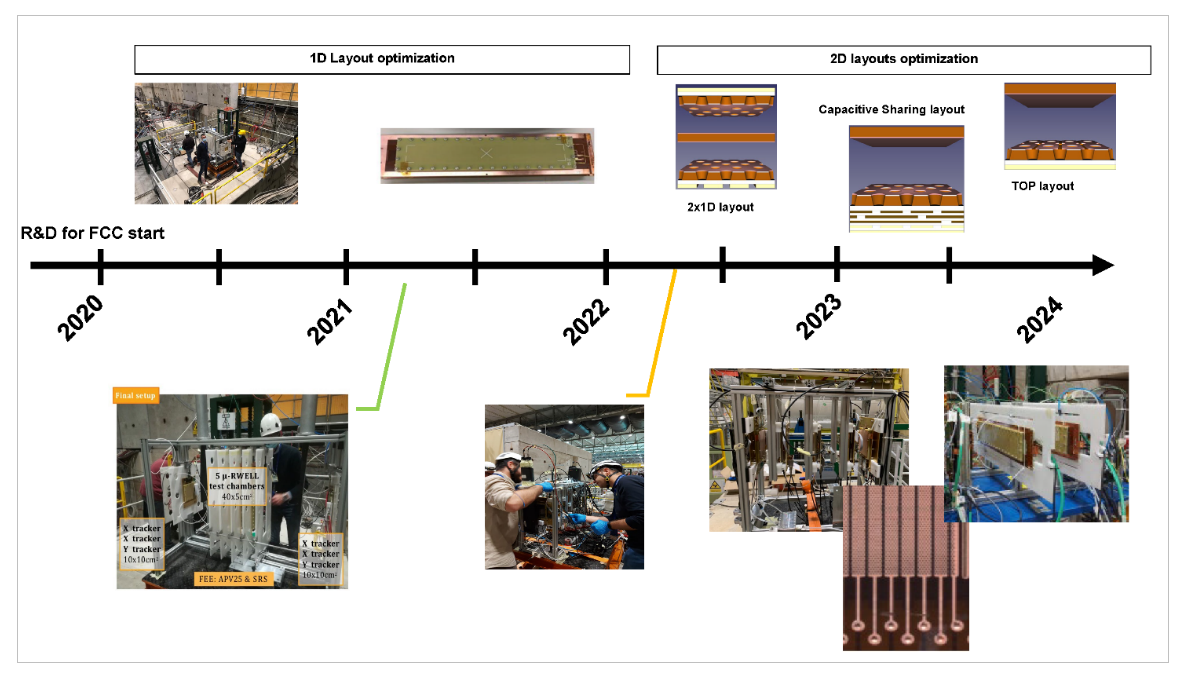
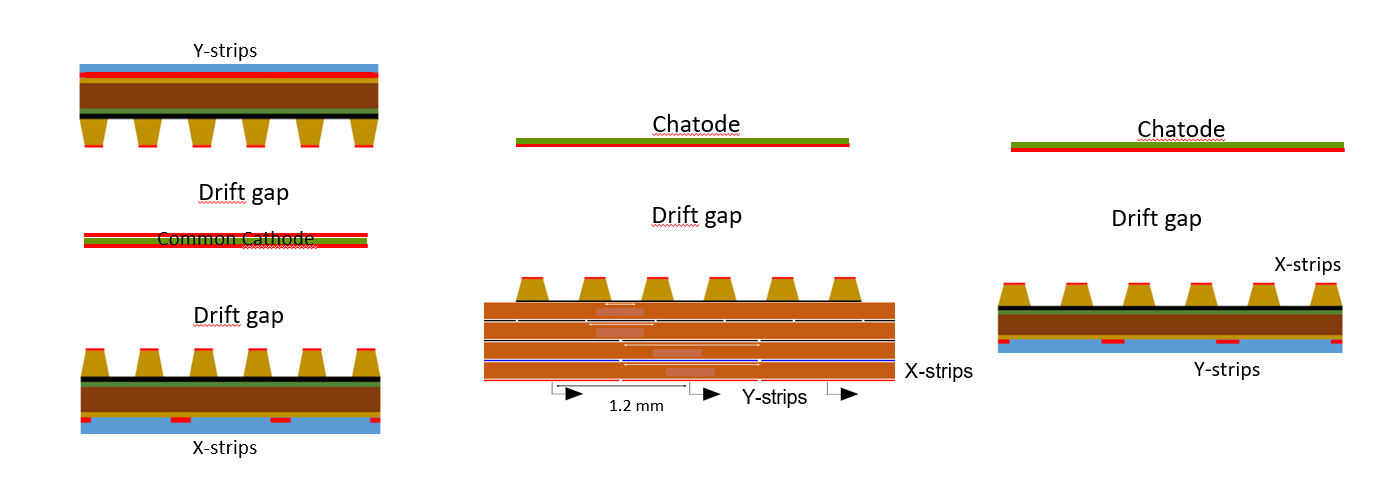
Three configurations are under study:
-
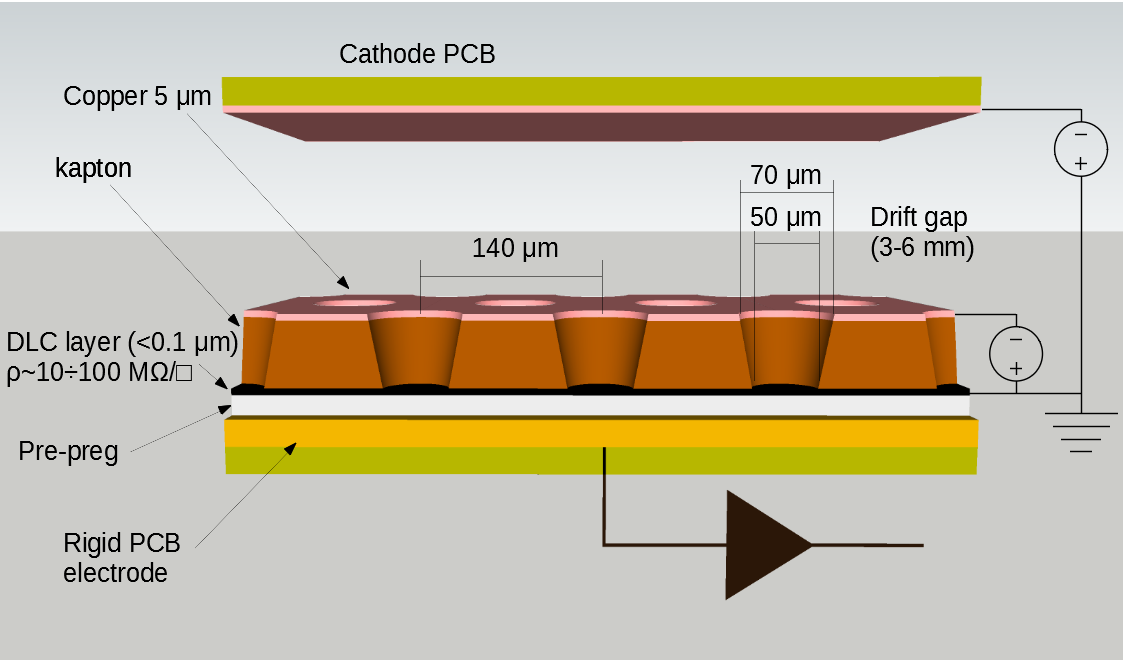
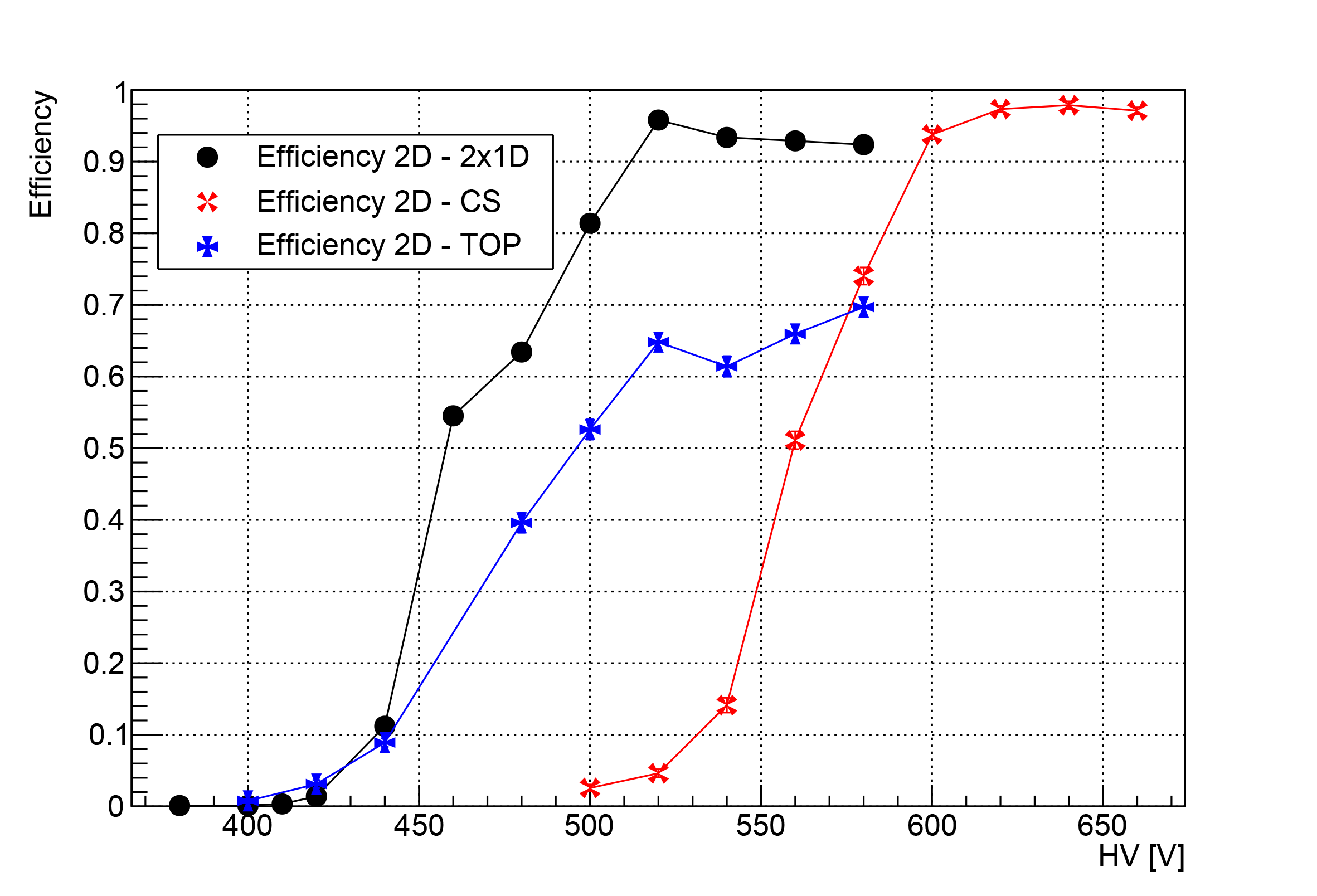
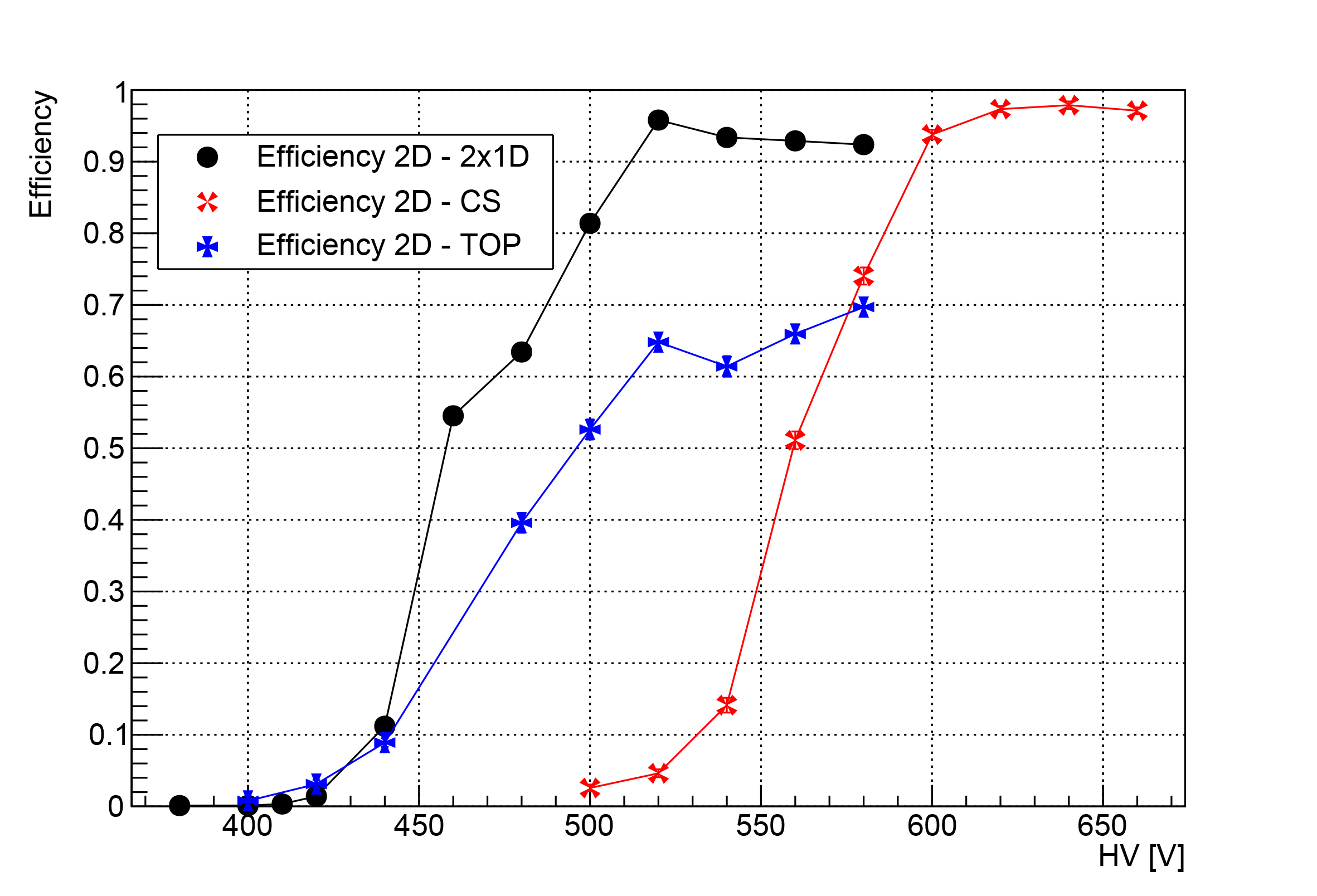
Coupled 1-D µ-RWELL: two standard 1-D detectors with a common cathode, offering simplicity and operation at standard gas gain due to completely separated readout strip views.
-
2-D µ-RWELL with patterned top electrode: Uses a standard 1-D readout and a strip-patterned top electrode for the second coordinate, avoiding the need for higher gas gain.
-
2-D µ-RWELL with capacitive-sharing anode: Provides high spatial resolution with a significative reduction of the number of readout channels.
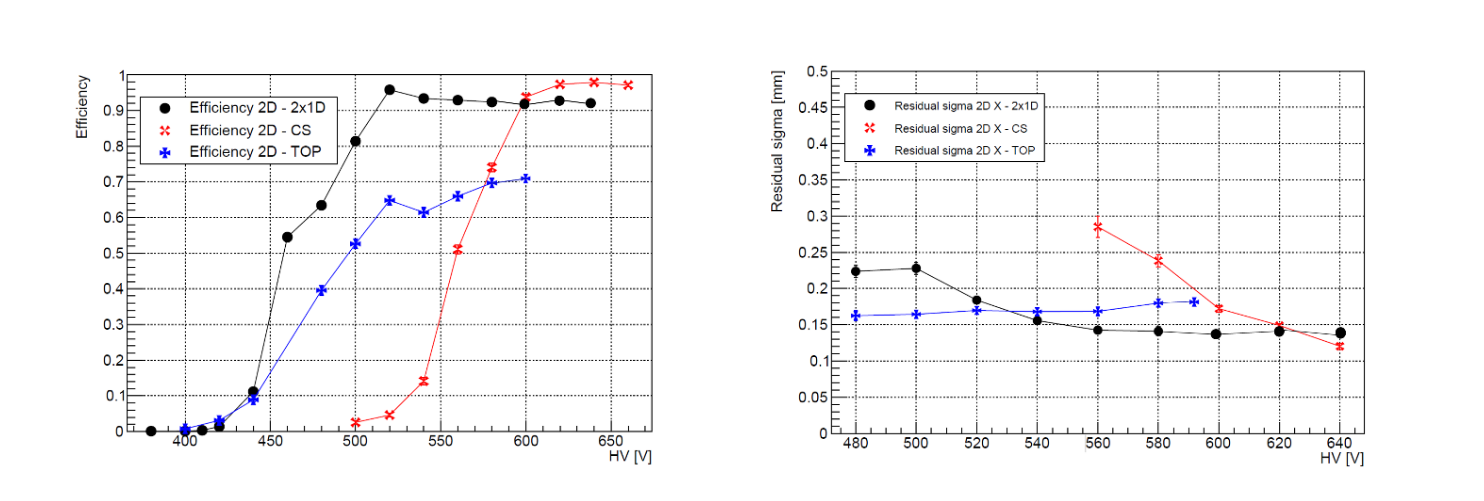
The layouts have been tested with a muon beam at CERN. All three layouts demonstrated good spatial resolution. However, the second layout showed an efficiency plateau of ~70% due to dead areas on the segmented amplification electrode. The third layout achieves very good performance despite requiring a higher high voltage on the amplification stage. R&D efforts will continue to optimize layouts for 2-D readout performance and their operational stability.