The purpose
The mission of DODAS is to act as a cloud enabler for scientists seeking to easily exploit distributed and heterogeneous clouds to process, manipulate or generate data. Aiming to reduce the learning curve, as well as the operational cost of managing community specific services running on distributed cloud, DODAS completely automates the process of provisioning, creating, managing and accessing a pool of heterogeneous computing and storage resources.
Within the EOSC-hub project "DODAS - Thematic Service" is providing both the PaaS core services and an Enabling Facility provided by Cloud@CNAF and Cloud@ReCaS-Bari. Even though DODAS PaaS core layer can be used to exploit any cloud in a standalone manner, we foresee that a user might benefit of a freely accessible Enabling Facility where to test a customisation and/or simply try out how DODAS behaves etc.
The core component responsible for the deployment creation and management is the InfrastructureManager(IM).
IM is a tool that ease the access and the usability of IaaS clouds by automating the VMI selection, deployment, configuration, software installation, monitoring and update of Virtual Appliances. It supports APIs from a large number of virtual platforms, making user applications cloud-agnostic. In addition it integrates a contextualization system to enable the installation and configuration of all the user required applications providing the user with a fully functional infrastructure.
Components
As introduced, DODAS manages container based applications and thus it relies on container orchestration for application deployment and management.The architecture has been built on top Kubernetes.The integration of Kubernetes resources in the DODAS is done via:
- The creation of a plain Kubernetes cluster through a configurable Ansible role that takes care of all the needed steps from the initialization with “kubeadm” tool until the deployment of the kubernetes dashboard or metric server.
The deployment of the applications that leverages the templating capabilities of Helm. A full integration of Helm with TOSCA is provided although the capability to run Helm on top of any pre-existing kubernetes instance has also been preserved. - The applications are structured in such a way that, through the very same base template structure, different flavors of the same cluster can be deployed. For instance one can activate a certain type of shared filesystem to be used by putting a flag at Helm configuration level (so called “Helm values”). In addition multiple applications can be combined as needed with the Helm dependency system, where the child application will wait for the parent to be completely deployed before starting its own installation. The Helm charts integration in the TOSCA template has been possible thanks to the usage of Ansible roles which take care of compiling Helm values only when the cluster has been automatically created and thus all the parametrized information are known. All the produced charts are documented following the best practices adopted by official projects in the Helm, so that anyone interested can easily fix or add features to the existing charts here.
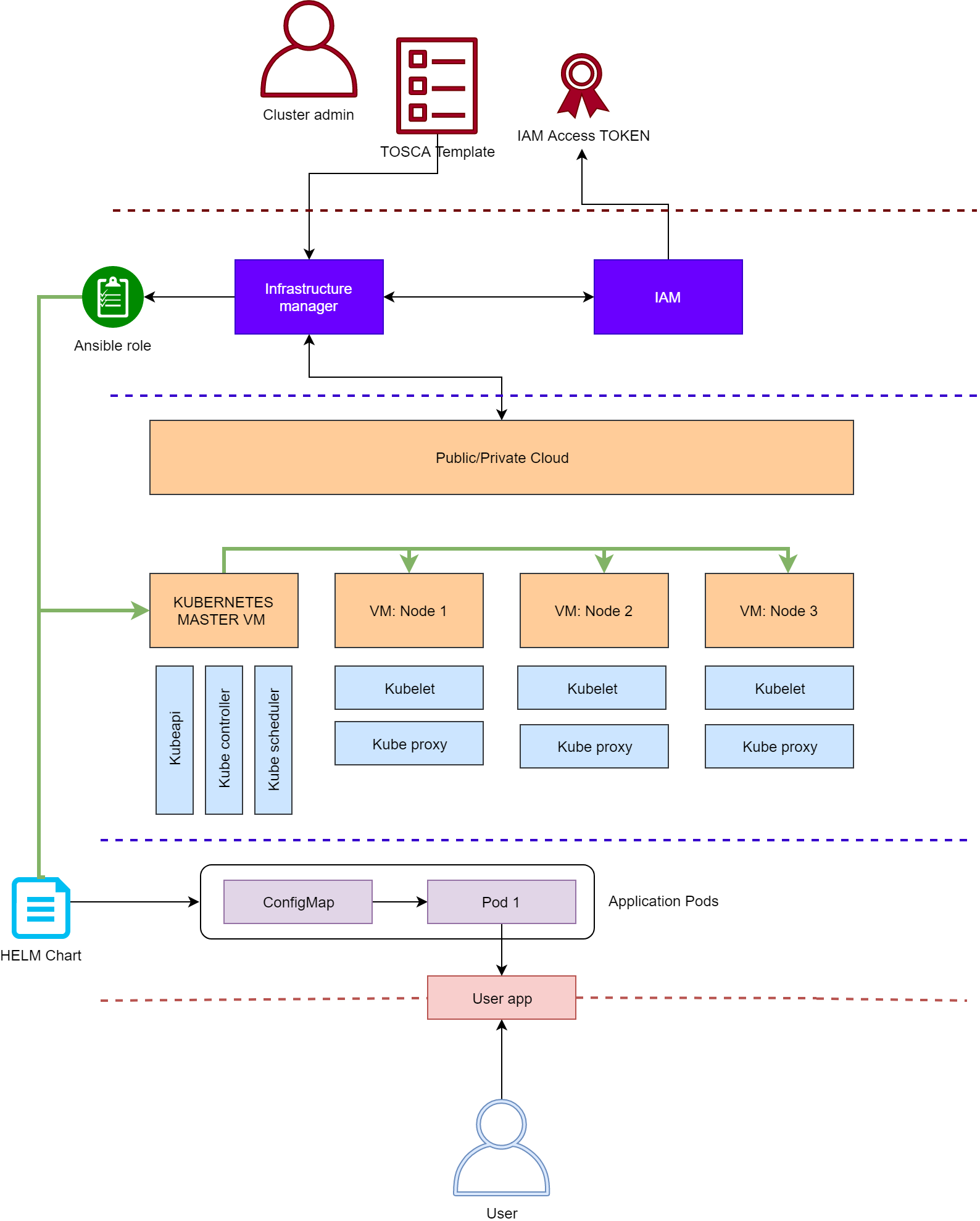
The complete flow can be summarized as follow:
- Admins authenticate with the Infrastructure Manager:
- using either username and password or a IAM access token
- IM uses the TOSCA template provided by the admin to deploy:
- a k8s cluster
- one or more helm charts on top of it:
- using the helm install ansible role here:
- kubectl create of any manifest is also supported by an ansible role
- any other action supported or integrated into a tosca node type
- a k8s cluster
