Scientific Program
- Details
- Hits: 1856
The main tasks of this R&D is the development of different detectors basted on GEM technologies essentially for beam diagnostics. The use of GEM foils for detector construction started in Frascati on 2002 with the R&D for LHCb muon chambers M1R1.Since then, several triple GEM chambers have been built for different applications; the performance of them are described in this web site. This R&D is devoted not only to the detectors development but also to the readout electronics and power supply.
A summary of this R&D can be found in this article :
F.Murtas, Applications of triple GEM detectors beyond particle and nuclear physics
2014 JINST 9 C01058
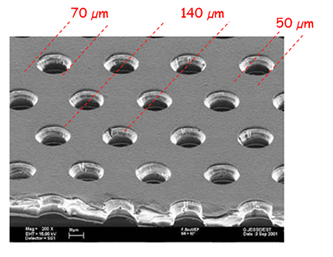 |
A Gas Electron Multiplier (F.Sauli, NIM A386 531) is made by 50 µm thick kapton foil, copper clad on each side and perforated by an high surface-density of bi-conical channels; |
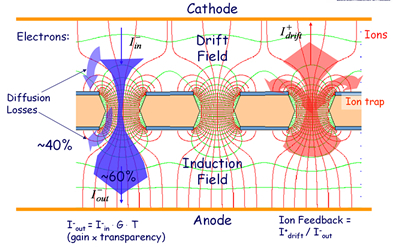 |
By applying a potential difference between the two copper sides, an electric field as high as 100 kV/cm is produced in the holes, acting as multiplication channels. |
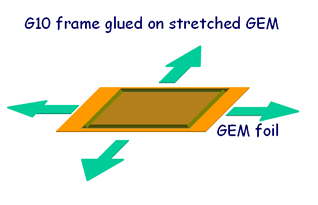
One of the main characteristics of GEM detectors built in Frascati is the stretching procedure. The GEM foils are placed on the apposite tool shown in the figure below and afterwards a frame (typically made in G10) is glued on top of it. |
|
  |
|
|
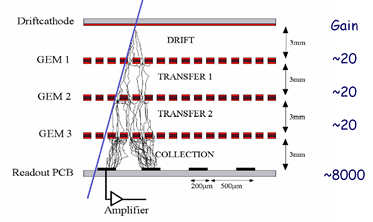 |
The picture on the left shows the electron cluster produced by a charged particle impinging a triple GEM detector through the GEM foils. The typical gain of this detector is 10⁴. |
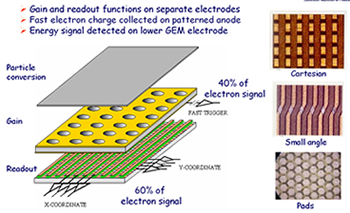 |
On the left the decoupling in the three main stages of this detector: particle conversion, signal amplification induction on the electrode pads with different readout scheme. |
