GEM for Fusion
- Details
-
Last Updated: Friday, 31 July 2015 11:28
Soft X-ray diagnostics for a burning plasma experiment have to be radiation tolerant, easily shielded, and must own both low sensitivity to neutrons and gammas and energy measurement capability. The general conception of these diagnostics should therefore evolve in the direction of pattern recognition for a real time feedback on the tokamak operation setting.
 |
|
The X-ray GEM detector built for the tokamak KSTAR, in collaboration between ENEA and INFN Frascati, is a compact, portable and flexible detector, fully shielded. The metallic case was developed to house the detector and the electronic boards, not only for mechanical protection and interface with steerable mechanical mounting on the port, but also for shielding it against electromagnetic and radiofrequency disturbances. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
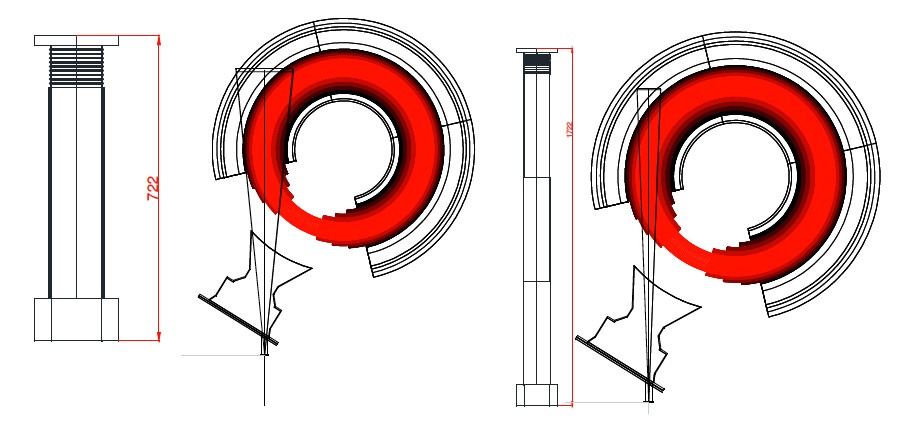
The installation on KSTAR, was designed as a pinhole camera, to see most of the core plasma, with adjustable magnification (from ×10 to ×30). The relative distance of the camera with respect to the port, where the pinhole is mounted, can be adjusted in the range 55÷165 cm to achieve the desired magnification
October (2013)
|
| |
|
|
 |
|
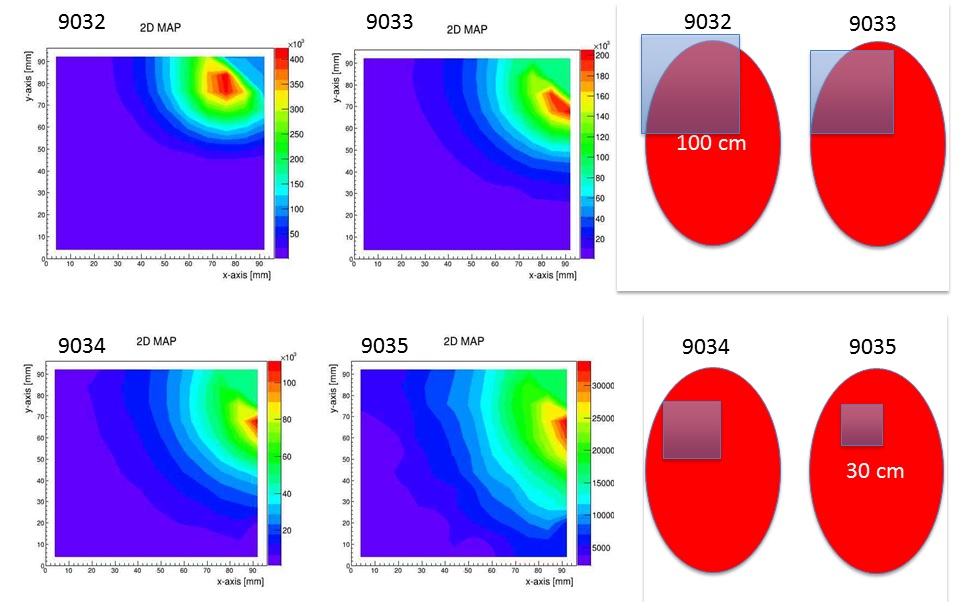
Soft X-Ray imaging of the KSTAR plasma core using the GEM system obtained at different magnifications, in the energy range 3÷15 keV: (left) experimental data; (right) corresponding schematic representations of the plasma cross section (red) and the field of view of the camera (partially transparent blue).
October (2013)
|
 |
|
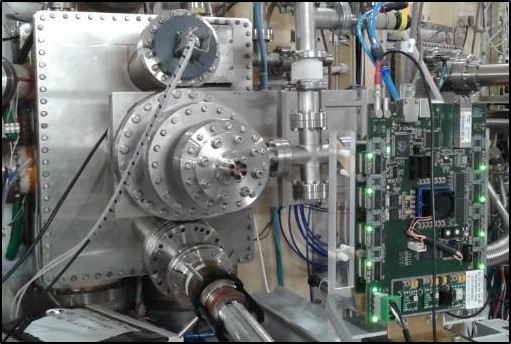
Another test has been performed in July 2015 at Frascati Tokamak FTU. The same type of GEM detector used at KSTAR has been placed in front of the port n5 as can be seen in the picture. |
| |
|
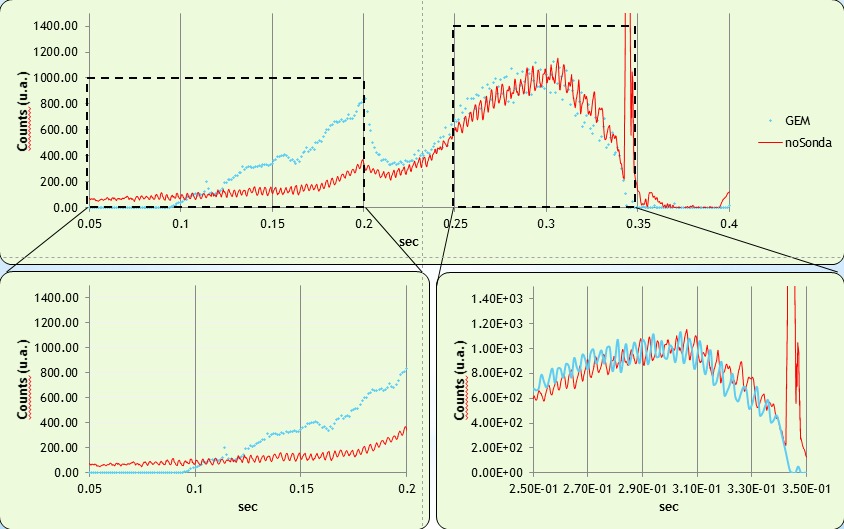
The GEM detector measurements shown a better sensitivity respect to the standard diagnostics used at FTU, especially during the current rising over a wider range.
In the picture the GEM (blu dots) and the standard diagnostic (red line)
During the plateau phase the detector is able to follow the oscillations in the Xray flux.
(July 2015)
|