GEM in Radiotherapy
- Details
- Last Updated: Wednesday, 12 February 2014 09:57
We built a prototype of new 2D gas dosimeter for IMRT dose checking. It is based on Gas Electron Multiplier (GEM) micropattern technology and has an anode and read-out electonics which allows to obtain a sub-millimiter resolution with an on line control of data acquisition. We show here also the first results obtained on small radiotherapy gamma beams coming from a clinical linac.
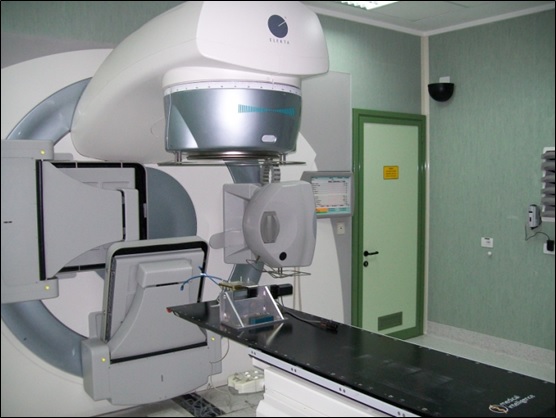 |
Mesaurements were performed on a IMRT clinical linac located at the radiotherapy department of Tor Vergata University General Hospital. | |
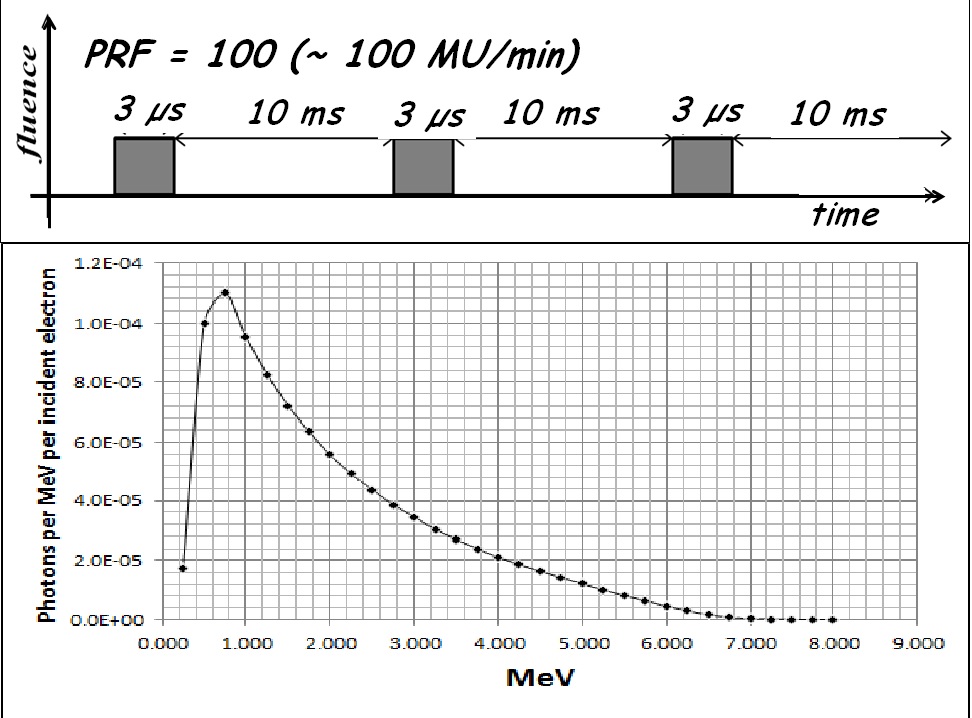 |
The linac used is the Elekta Synergy S with three working energies (6, 10, 18 MV photons). Gamma beam coming from a clinical linac has temporal pulsed structure with a variable frequency (a parameter known as PRF). Elekta Synergy S linac can work at 7 different values (6, 12, 25, 50, 100, 200, 400 Hz). Pulse width is 3 µs and the number of particles per pulse estimated is about 6.7 x 1010ph/(mm2 sec). | |
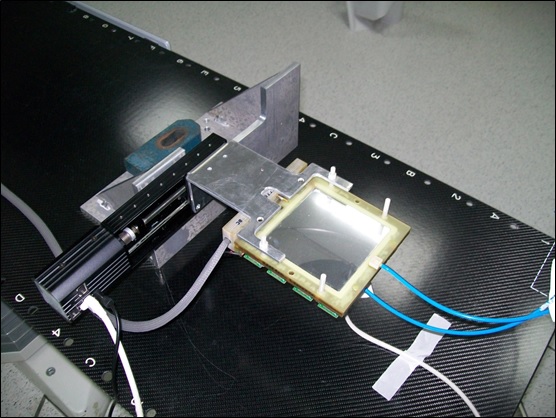 |
The detector was placed under a MV gamma beam coming from the linear accelerator. The ionization is produced mainly on the firts GEM foil. A very little fraction of the Copmton electron are backscattered in the active volume. The ones that comes near the GEM holes are multiplied and produce current pulse signals. So detector is able to work at very low efficiency but at the same time it provides a number of digital counts proportional to the photon beam fluence. Counts are linearly correlated to PRF which sets the number of MU/min. | |
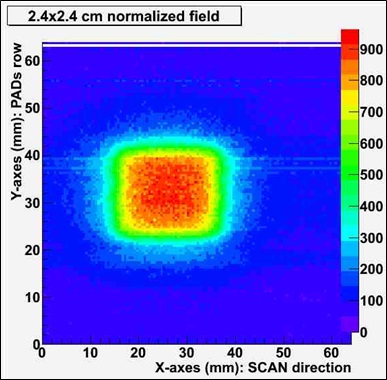 |
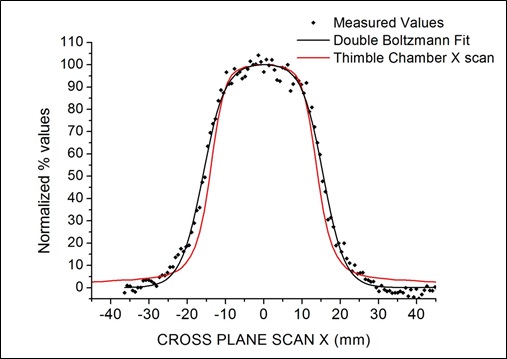
Our detector is mounted on a high precision linear motor (previous figure) so that the pads strip can scan in steps equal to the pitch. In this way a sensitive area of 9 x 9 cm2 is obtained. Several measurements were performend on small irradiation fields: 0.8 x 0.8 cm2, 2.4 x 2.4 cm2, 4.0 x 4.0 cm2. In the figure the 2D image of the gamma spot produced in 6 seconds. |
|
 |
 |
|||
| These plots show comparison between the X and Y profiles taken at the isocenter. | ||||

