Past news
ALICE studies of antinuclei at the LHC help Dark Matter searches in space
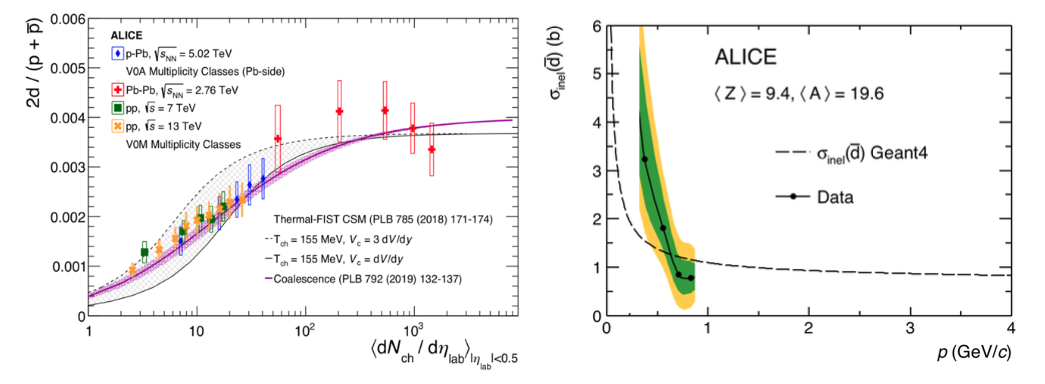
ALICE studies of antinuclei at the LHC help Dark Matter searches in space
Dark Matter (DM) is thought to account for approximately 80% of the matter in the Universe and is searched for in several experiments on Earth and in space (including AMS-02 and GAPS). The detection of low-energy antinuclei is a promising signal in the DM searches in space. Yet, in order to interpret a possible observation, a quantitative understanding of the antinuclei production and annihilation mechanisms within the interstellar medium is mandatory. These mechanisms can be studied using the LHC as an antimatter factory and the ALICE experiment as an antimatter detector. The INFN groups play an important role in these studies. The ALICE collaboration has recently published a measurement of the production of (anti)deuterons in proton-proton collisions, as well as in other colliding systems, providing strong constraints to the production models, shown as overlaid curves in the left panel of the figure, which can then be used to predict the antinuclei fluxes in space. The Collaboration has also measured for the first time the antideuteron inelastic cross section at low energy (right panel), using the ALICE detector as an absorber. The momentum range covered in this measurement is of particular relevance to interpret observations in space in terms of DM candidates. Additionally, these measurements help understanding the low-energy antimatter-matter annihilation processes.
CERN Media Update:
https://home.cern/news/news/physics/fresh-antimatter-study-alice-collaboration-will-help-search-dark-matter
Further reading:
Measurement of the low-energy antideuteron inelastic cross section:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2005.11122.pdf
(Anti-)Deuteron production in pp collisions at √ s = 13 TeV:
2019 CNAF report published online

2019 CNAF report published online: the contribution of experiments in CSN3
The annual CNAF report, for 2019, is online at this link. Previous editions are available at this link. Three experiments belonging to the CSN3 contributed to this edition, with the following reports:
- ALICE computing at the INFN CNAF Tier1
- From experimental nuclear astrophysics to nucleosynthesis simulations with ASFIN
- The NEWCHIM activity at CNAF for the CHIMERA and FARCOS devices
In 2019, the ASFIN, FOOT, FAMU, NUCLEX, GAMMA, n-TOF and NEWCHIM experiments benefited from the calculation resources offered by CNAF, for a total of about 9400 HS06, 150 TB of disk and 1900 TB of tape. To these must be added the ALICE experiment with about 60000 HS06, 6000 TB of disk and 12000 TB of tape.
Third meeting on heavy ions physics at high energies

"The Third Meeting on Physics with Heavy Ions at High Energies" has been postponed. The new dates will be announced as soon as possible. The Organizing Committee has decided to pospone the meeting because of the Covid-19 restrictions.
Web page https://agenda.infn.it/event/21267/
New INFN external funding portal
 The new portal created by the External Funds Division (DFE) has been online since 15 April to optimize the search for information on funding opportunities offered by the various funding institutions, events and training opportunities, with direct links to research tools, including "Research Professional". The website allows one to access a public database that collects all the projects with funding received from the INFN on external funds.
The new portal created by the External Funds Division (DFE) has been online since 15 April to optimize the search for information on funding opportunities offered by the various funding institutions, events and training opportunities, with direct links to research tools, including "Research Professional". The website allows one to access a public database that collects all the projects with funding received from the INFN on external funds.
Applied Nuclear Physics Conference

13-18 September 2020
Praga - Repubblica Ceca
https://www.anpc2020.cz/